Treatments
Congestive Heart Failure Therapy
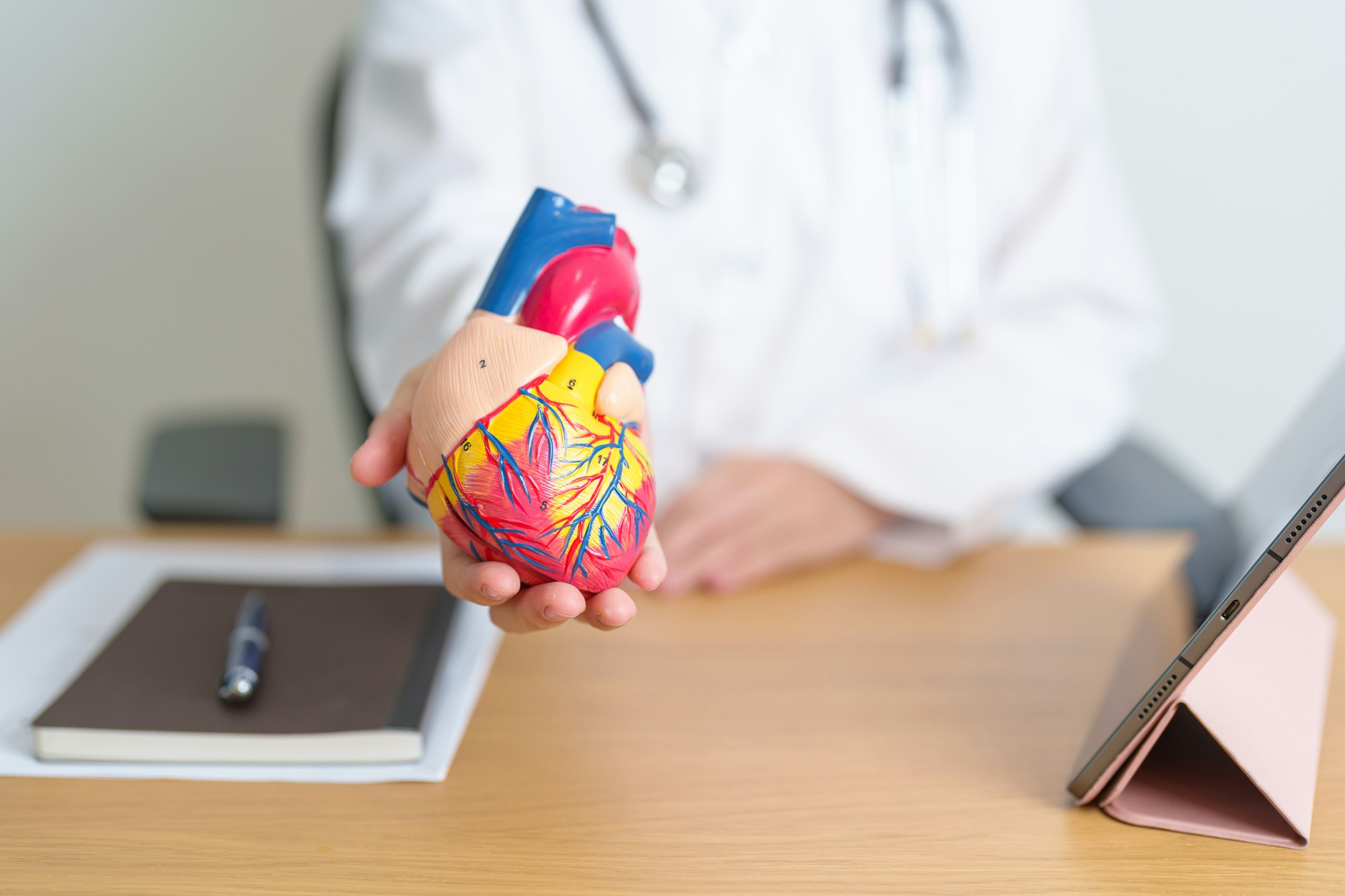
Congestive heart failure (CHF) is an imbalance in pumping function in which the heart fails to adequately maintain the circulation of blood. CHF does not mean that your heart has stopped or is about to stop working. It means that your heart is not able to pump blood the way it should.
The weakening of the heart’s pumping ability can cause blood and fluid to back up in your lungs, edema, tiredness and shortness of breath.
CHF is a serious condition affecting more than five million Americans. Caused by coronary artery disease, high blood pressure and diabetes, CHF treatment includes addressing these underlying causes as well as the use of medications. Common medications used are: ACE inhibitors, diuretics (water pills), vasodilators, digitalis preparations, beta-blockers, blood thinners, angiotensin II receptor blockers, calcium channel blocker, and potassium. Heart transplant is also considered, if all else fails.
For more information on congestive heart failure therapy, visit the U.S. National Library of Medicine’s Website.